Go Green DIY’s professional Team will provide you with more information about the windows and doors and how they can save you money through out a year.
Types Of Frames
Improving the thermal resistance of the frame can contribute to a window’s overall energy efficiency, particularly its U-factor. There are advantages and disadvantages to all types of frame materials, but vinyl, wood, fiberglass, and some composite frame materials provide greater thermal resistance than metal.
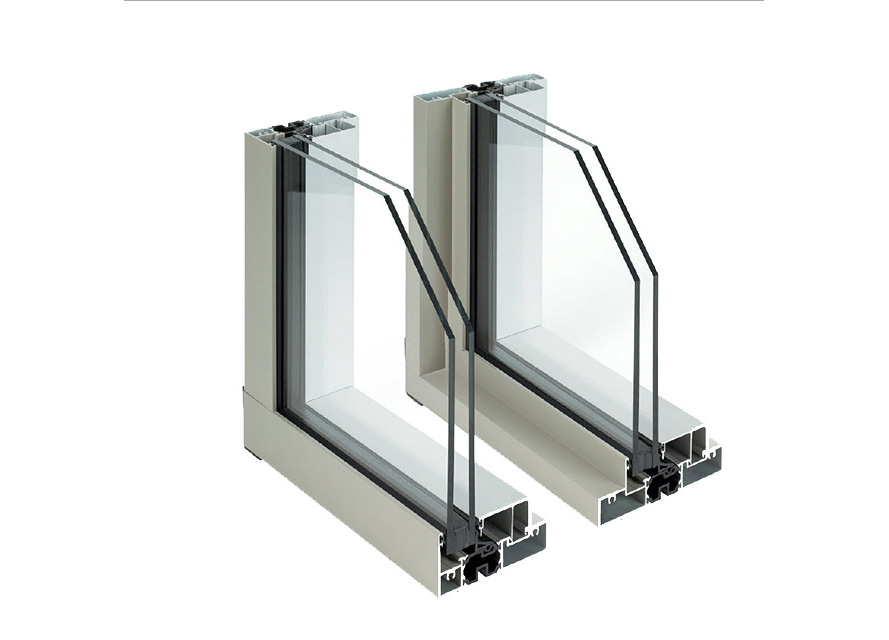

Aluminum Frames
Although very strong, light, and almost maintenance free, metal or aluminum window frames conduct heat very rapidly, which makes metal a very poor insulating material. To reduce heat flow and the U-factor, metal frames should have a thermal break — an insulating plastic strip placed between the inside and outside of the frame and sash.
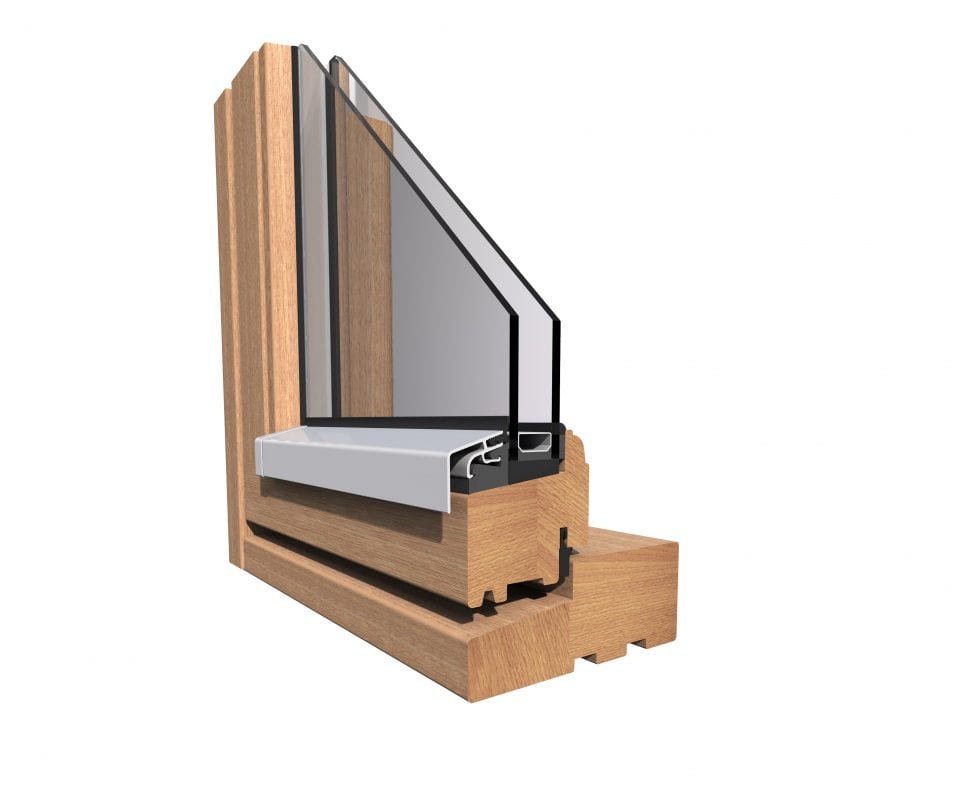
Composite and Wood Frames
Composite window frames consist of composite wood products, such as particleboard and laminated strand lumber. These composites are very stable, they have the same or better structural and thermal properties as conventional wood, and they have better moisture and decay resistance.
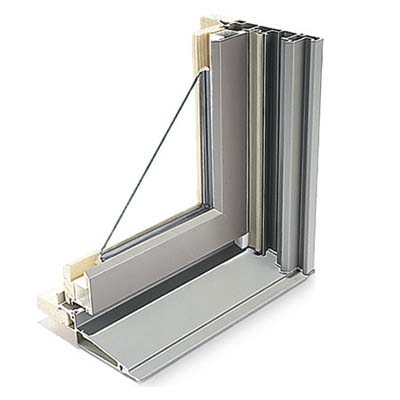

Fiberglass Frames
Fiberglass window frames are dimensionally stable and have air cavities that can be filled with insulation, giving them superior thermal performance compared to wood or uninsulated vinyl.
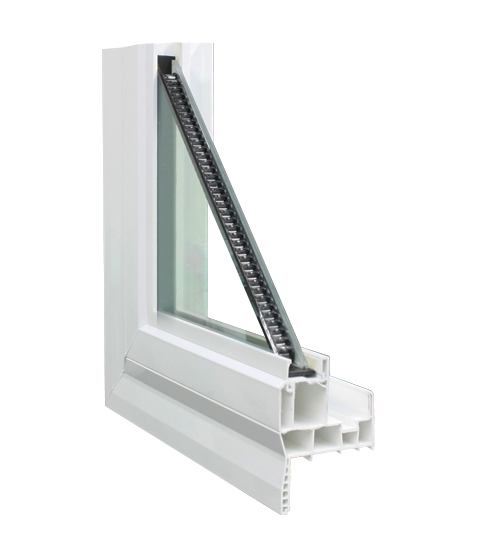

Vinyl Frames
Vinyl window frames are usually made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with ultraviolet light (UV) stabilizers to keep sunlight from breaking down the material. Vinyl window frames do not require painting and have good moisture resistance.
The hollow cavities of vinyl frames can be filled with insulation, which makes them thermally superior to standard vinyl and wood frames.
